Abstract
Background: Molecular analyses of risk cohorts in adults with B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (ALL) has lagged behind progress in children with B-cell ALL. Two widely recognized prognostic variables are mutations in BCRABL1 and in IKZF1 with mutation frequencies of about 25 and 50 percent in unselected adults.
Aims: Interrogate the mutation topology of adult B-cell ALL and compared the discrepancies of cohorts with different BCRABL1 and IKZF1 status.
Methods: We performed targeted DNA-sequencing in 226 newly-diagnosed adults with B-cell ALL including whole-genome in 8 paired samples (at diagnosis and complete remission) and whole-exome sequencing in 13 paired samples (at diagnosis and complete remission). 7 paired samples (at diagnosis and relapse) were detected by whole-exome sequencing to study relapse mutation topology.
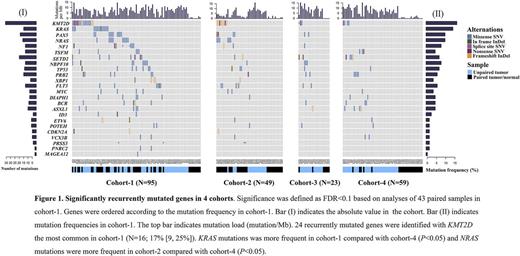
Results: We identified 2285 mutations in 791 genes (median, 11 mutations per subject). 190 subjects (84%; 95% confidence interval [CI],[79, 89%]) had ≥2 mutations. Most mutations occurred at low frequencies except KMT2D (also termed MLL2; N=31; 14% [9, 19%]; (Figure). We found 4 new mutated genes, PRB2 (N=13; 6% [3, 9%]), NBPF10 (N=12; 5% [2, 8%]), TSFM (N=8; 4% [1, 7%]) and DIAPH1 (N=8; 4% [1, 7%]). Subjects were divided into the 4 most common ALL genotypes to interrogate how other mutations interact with these genotypes: (1) BCRABL1- negative, IKZF1 wild-type (N=95; 42%, cohort-1); (2) BCRABL1- negative, IKZF1 deletion (N=49; 22%, cohort-2); (3) BCRABL1 -positive, IKZF1 wild-type (N=23; 10%, cohort-3); and (4) BCRABL1 -positive, IKZF1 deletion (N=59; 26%, cohort-4). KRAS mutations in cohort-1 were more frequent than in cohort-4 (15% [8, 22%] vs. 0 [0, 6%]; P =0.002). NRAS mutations in cohort-2 were more frequent than in cohort-4 (12% [3, 21%] vs. 0 [0, 6%]; P =0.007). No other pair-wise comparison was statistically significant. In relapse samples, frequency of the significant recurrent mutations was higher in subjects in the BCRABL1 -negative cohort compared with the -positive cohort (median of 1; range, 0-9 vs . median of 0.5; range, 0-4; P =0.019). NBPF10 was the only novel mutated gene found at relapse. Acquisition of new mutations of founder clone and expansion of previously undetectable sub-clones at diagnosis were detected at relapse.
Conclusions: These data provide insights into the mutation topology of adults with B-cell ALL, identify diverse mutations some of which correlate with BCRABL1 and IKZF1 mutation status as well as 4 new mutated genes and indicate some relapse patterns. (Trial registered in the Beijing Municipal Health Bureau Registration N: 2007-1007 and the Chinese Clinical Trial Registry [ChiCTR-OCH-10000940 and ChiCTR-OPC-14005546]; http://www.chictr.org.cn)
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal